
Made by Oliver for Entimology Pest insect control assignment
What are Emerald Ash Borer's?
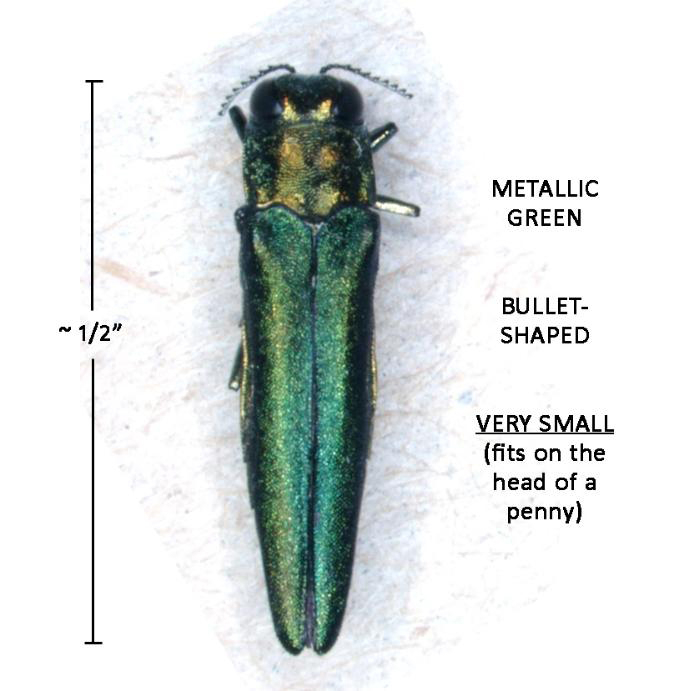
Emerald Ash Borers(abbr. EAB) are a type of Buprestid(Buprestidae), also known as Jewel Beetle, native to Asia. They are identifyable by their small size, bullet shaped body, and metallic green color.
Natural Habitat
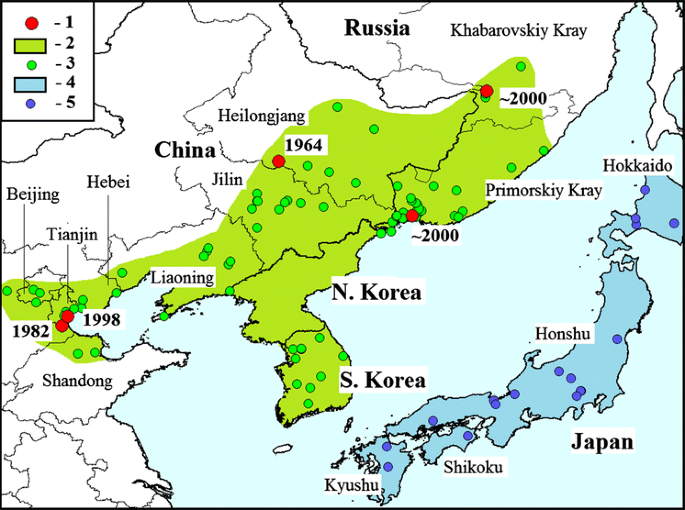
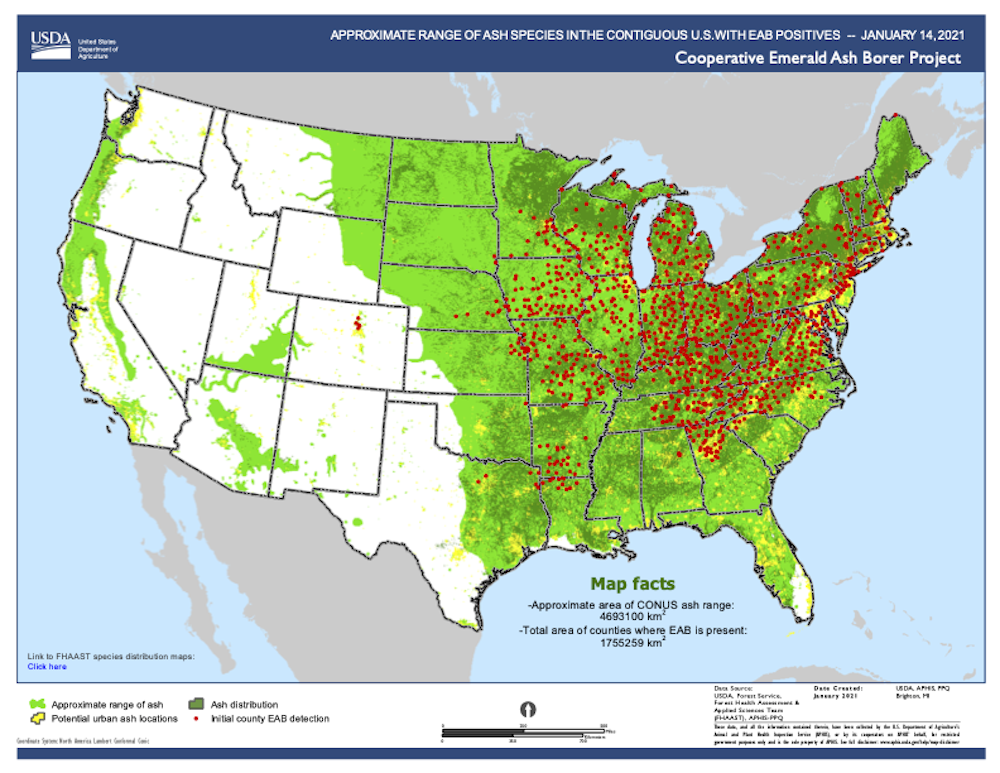
EAB. 's natural habitat is in Northestern Asia, ranging from Russia, Mongolia, northern China, Japan, and Korea. In the US the EAB has spread throughout the whole left side, from eastern montana to northern florida and up to maine. Its also located in the forests of the west coast as well.
Life Cycle
The damage to trees are caused by their life cycle. The parent lays eggs on the bark of the ash tree, the larvae hatch and burrow into the tree, the adults chew at the bark in a D shape, then the adult seeks out a new ash tree for its young. The tree is obviously hurt by this process and will die after a couple years.

How are they controlled Chemically?
Imidacloprid, dinotefuran, emamectin benzoate, and azadirachtin are the main chemicals used to control EAB. Imidacloprid is the most affordable and common one, It can be bought in grocery stores and is poured on the roots of the tree.

How are they controlled Biologically?
Woodpeckers and Parasitoids are the main ways in which we are dealing with EAB. Spathius agrili, Tetrastichus planipennisi, Oobius agrili, and Spathius galinae have all been released into the us in order to fight off the EAB.

credits/rubric | wild rice